| The urinary bladder stores urine until it is ready to be voided. Click Here For Microscopic Image |
The urinary bladder is essentially an organ for storing
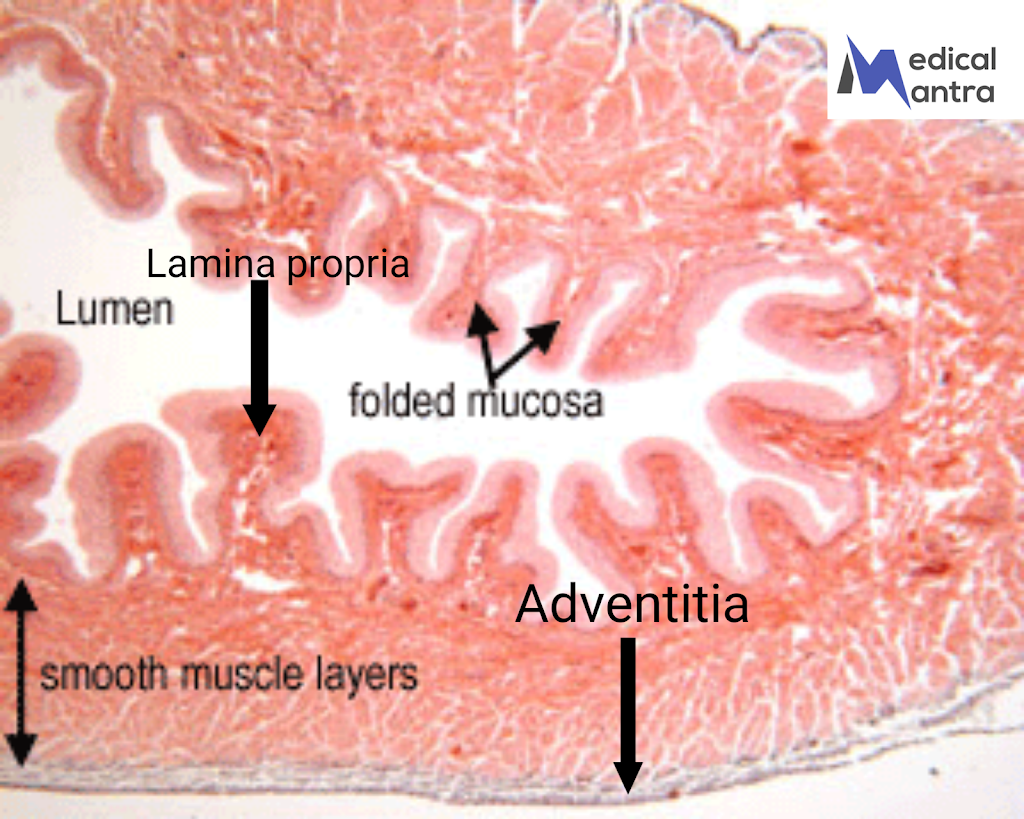
urine. Histologically, The urinary bladder is made up of different layers. The innermost layer of urinary bladder is called the mucosa, which consists of a type of epithelium called transitional epithelium or urothelium. Below the mucosa is the lamina propria, a connective tissue layer. Surrounding the lamina propria is a thick layer of smooth muscle. The back of the Urinary bladder is covered by a layer called the serosa, while the front of the urinary bladder has an outer layer called the adventitia, which helps the urinary bladder stick to the front wall of the abdomen . The Urinary Bladder has folds on it’s mucosal layer called rugae , these folds allow urinary bladder to expend . when urinary bladder filled with urine the large, round, dome-shaped cells of the transitional epithelium become stretched and change their
morphology to become flattened.
Layers of the Urinary Bladder:
1. Mucosa:
- The innermost layer of urinary bladder composed of transitional epithelium (urothelium), which allows the urinary bladder to stretch. It is supported by an underlying connective tissue layer called the lamina propria.
- The mucosa forms numerous folds that disappear as the bladder fills with urine.
- The cells of the transitional epithelium change shape from large, round, dome-shaped cells when the urinary bladder is empty to flattened cells when stretched.
2. Lamina propria: It lies beneath the mucosa and can be divided into two layers:
- Superficial layer: Dense, irregular collagenous connective tissue.
- Deeper layer: Looser connective tissue composed of a mixture of collagen and elastic fibers.
- The lamina propria does not contain glands, except near the urethral orifice, where mucous glands may be present.
3. Muscular coat (detrusor muscle): Composed of three interlaced layers of smooth muscle that contract to expel urine. smooth muscle layer is absent at the neck region The layers are as follows:
- Inner longitudinal layer: Thin layer of smooth muscle fibers oriented longitudinally.
- Middle circular layer: Thick layer of smooth muscle fibers arranged in a circular pattern. It contains elastic fibers and forms the internal sphincter muscle around the neck of the bladder.
- Outer longitudinal layer: Thin layer of smooth muscle fibers oriented longitudinally.
4. Adventitia: The outermost layer of the bladder wall, composed of dense, irregular collagenous connective tissue with elastic fibers. Some regions may have a serosa, which is a peritoneal covering, while others may be surrounded by fat.
Parts of the Urinary Bladder:
1. Body:
- The larger region of the bladder that expands to store urine.
- The body of the bladder has the capacity to stretch as it fills with urine.
2. Neck:
- The smaller region of urinary bladder that connects the bladder to the urethra.
- The neck contains the internal sphincter muscle, which helps control the flow of urine into the urethra.
Functions of the Urinary Bladder:
1. Urine storage:
- The urinary bladder serves as a temporary reservoir for urine until the pressure within the bladder reaches a certain level, triggering the urge to urinate.
- The detrusor muscle relaxes, and the bladder contracts to expel urine during voiding.
2. Accommodation of cell shape:
- The transitional epithelial cells in the bladder have specialized regions called plaques, interspersed by normal cell membrane regions.
- When the bladder is empty, the plaques are folded into irregular, angular contours, but they disappear as the cell becomes stretched during bladder filling.
3. Osmotic barrier:
- The urothelial cells with plaques act as barriers between the urine and the underlying lamina propria.
- Plaques are impermeable to water and salts, preventing their passage between the urine and connective tissue.
4. Sphincter muscles: The bladder has two sphincter muscles involved in the control of urination:
- Internal sphincter muscle: A ring of smooth muscle located at the neck of the bladder. It remains contracted to prevent the flow of urine until the pressure in the bladder is sufficient to initiate voiding.
- External sphincter muscle: Located in the urogenital diaphragm, it is composed of skeletal muscle fibers. This sphincter is under voluntary control and helps regulate the flow of urine from the bladder into the urethra.
5. Trigone: A triangular region of the bladder defined by the orifices of the two ureters and the urethra.
- The mucosa of the trigone remains smooth and does not form folds like the rest of the bladder.
- The trigone has a different embryonic origin compared to the rest of the bladder.