| The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ that is the site of maturation of T lymphocytes For More Histological Images Click Here |
General Overview of The Thymus :
- The thymus is a small encapsulated organ situated in the superior mediastinum.
- The thymus of two lobes and extends over the great vessels of the heart.
- Each lobe originates separately in the third (and possibly fourth) pharyngeal pouches during embryonic development.
- The thymus grows until puberty, after which it starts to involute (atrophy) and becomes infiltrated by adipose cells.
- However, The thymus may continue to function even in older adults.
Structure of The Thymus:
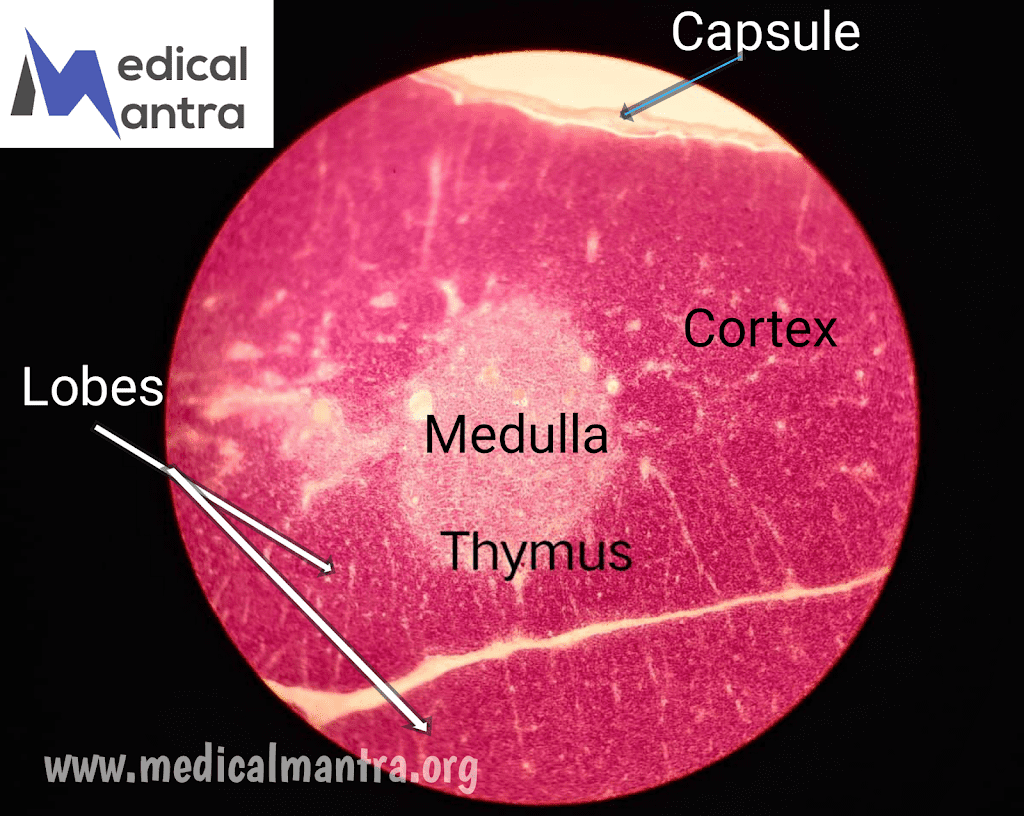
- The thymus is composed of a cortex and a medulla, with the medullae of adjacent lobes being confluent.
- The cortex appears darker histologically due to a high number of T lymphocytes (thymocytes), which undergo proliferation and instruction to become immunocompetent T cells.
- The medulla stains lighter than the cortex and contains fewer lymphocytes.
- The thymus is enclosed by a capsule composed of dense, irregular collagenous connective tissue that sends septa into the lobes, subdividing them into incomplete lobules.
Layers of The Thymus:
1. Cortex:
- Darker histologically due to the presence of numerous T lymphocytes (thymocytes).
- Houses macrophages, dendritic cells, and epithelial reticular cells (thymic epithelial cells).
- Developing T cells undergo extensive proliferation and instruction in the cortex to become immunocompetent T cells.
- Epithelial reticular cells (Type I, Type II, and Type III cells) isolate the cortex from the rest of the body.
- Type II cells form a cyto-reticulum that subdivides the cortex into small compartments filled with lymphocytes.
2. Medulla:
- Stains lighter than the cortex due to a lesser population of lymphocytes.
- Contains macrophages, dendritic cells, a small population of B cells, and a large number of endothelially derived epithelial reticular cells.
- Epithelial reticular cells (Type IV, Type V, and Type VI cells) contribute to the formation of the medulla.
- Hassall corpuscles, formed by Type VI cells, are characteristic features of the medulla and increase in number with age.
Vascular Supply of The Thymus:
- The thymus receives numerous small arteries that enter the capsule and distribute throughout the organ via trabeculae.
- Capillaries form a blood-thymus barrier in the cortex, preventing developing T cells from contacting blood-borne macromolecules.
- Self-macromolecules, however, are allowed to cross the blood-thymus barrier, possibly for the elimination of T cells programmed against self-antigens.
- The cortical capillary network drains into small venules in the medulla.
- Newly formed T cells leave the vascular supply at the corticomedullary junction and migrate through the cortex and medulla before exiting the thymus as naïve T cells.
Functions of The Thymus:
- The thymus plays a vital role in T cell development and maturation.
- Developing T cells undergo proliferation, expression of surface markers, and differentiation into T cell subtypes.
- T cells are tested for their ability to recognize self-MHC molecules and self-epitopes.
- T cells unable to recognize self-MHC molecules or programmed against self-macromolecules undergo apoptosis.
- Epithelial reticular cells produce factors such as AIRE and thymic stromal lymphopoietin that facilitate T cell proliferation, activation of dendritic cells, and differentiation.
- Hormones from extrathymic sources influence T cell maturation, including adrenocorticosteroids, thyroxin, and somatotropin.
Note: For More detailed notes on Thymus keep following our website we will upload soon . Thank You For Your Support.