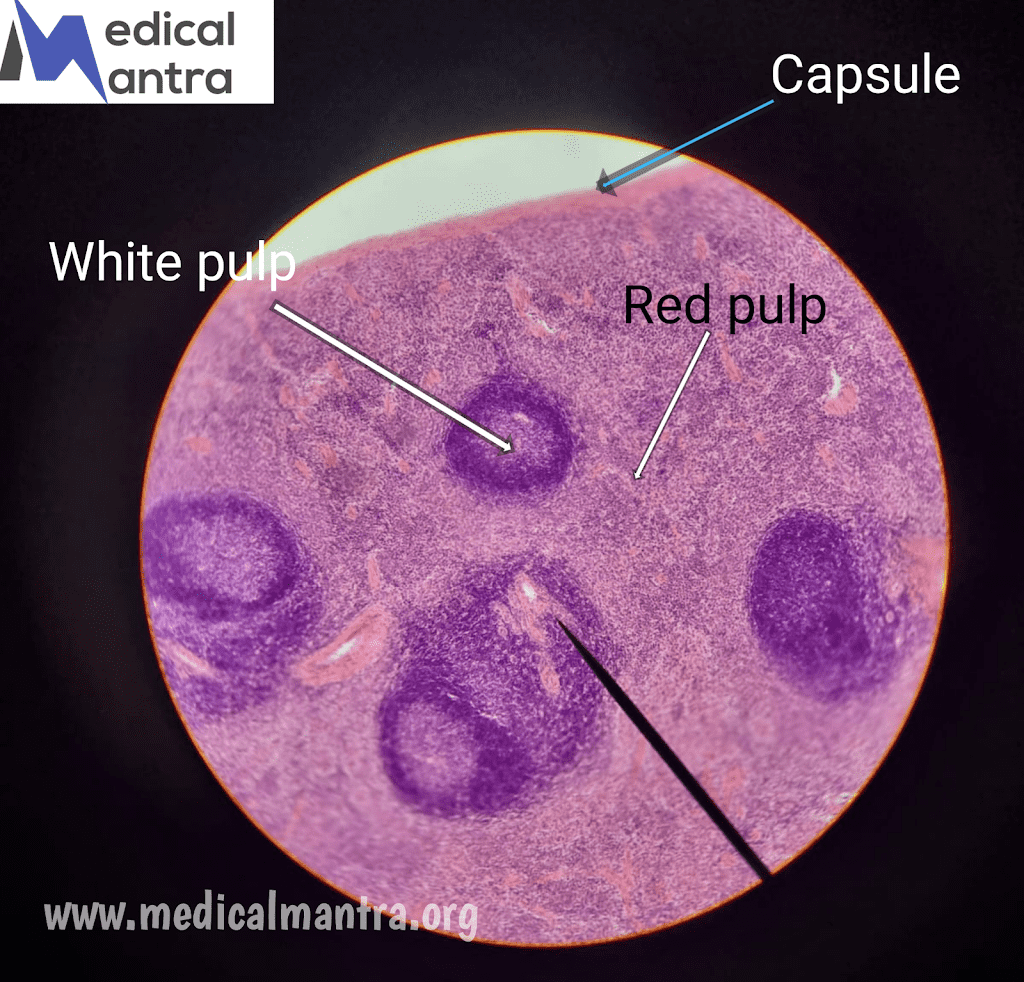
| The spleen, the largest lymphoid organ in the body, is invested by a collagenous connective tissue capsule; it has a convex surface and a concave aspect, known as the hilum. Click Here For More Microscopic Images |
General Information of Spleen:
- The spleen is the largest lymphoid organ in the body.
- It weighs approximately 150 g in an adult individual.
- It is located in the upper left quadrant of the abdominal cavity, within the peritoneum.
- The spleen functions in immune responses, blood filtration, and the destruction of old red blood cells and platelets.
- During fetal development, the spleen is involved in the production of blood cells.
Structure of Spleen:
- The spleen is surrounded by a dense, irregular fibroelastic connective tissue capsule.
- The capsule is covered by visceral peritoneum, which provides a smooth surface for the spleen.
- The spleen has a convex surface and a concave aspect known as the hilum.
- The hilum is the site where arteries, veins, and lymph vessels enter and leave the spleen.
- Trabeculae, arising from the capsule, carry blood vessels into and out of the spleen.
- The spleen has a three-dimensional network of reticular fibers and reticular cells, which form its architectural framework.
- The splenic parenchyma consists of white pulp and red pulp.
- White pulp is mainly composed of lymphocytes, while red pulp contains splenic sinuses and splenic cords.
Regions and Layers of Spleen:
White pulp:
- It is composed of periarterial lymphatic sheath (PALS) and lymphoid nodules.
- PALS surrounds the central artery and contains T lymphocytes.
- Lymphoid nodules are composed of B cells and can have germinal centers.
- Marginal zone: It separates the white pulp from the red pulp and contains plasma cells, T and B lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
Red Pulp:
- Red pulp consists of splenic sinuses and splenic cords.
- Splenic sinuses have fusiform endothelial cells with spaces between them.
- Reticular fibers surround the sinuses, and macrophages are numerous in their vicinity.
- Splenic cords are a loose network of reticular fibers with extravasated blood.
- Macrophages in the red pulp phagocytose blood-borne antigens, bacteria, and old platelets and erythrocytes.
Blood Supply and Circulation of Spleen:
- Vascular Supply: The spleen is supplied by the splenic artery and drained by the splenic vein, both entering and leaving the spleen at the hilum.
- Trabecular Arteries: Branches of the splenic artery, called trabecular arteries, penetrate the capsule and carry blood into the spleen.
- Central Artery: The central artery, located in the periarterial lymphatic sheath, gives rise to follicular arterioles, supplying the lymphoid nodules.
- Red Pulp Circulation: From the central artery, blood flows into the red pulp through penciller arterioles. Blood is then drained into splenic sinuses and eventually leaves the spleen through the splenic vein
Functions of Spleen:
Immunological Functions:
- Antibody Formation: The spleen plays a role in the production of antibodies by B cells in the lymphoid nodules.
- T-Cell and B-Cell Proliferation: The white pulp of the spleen supports the proliferation of T cells and B cells in response to antigens.
- Immune Response Activation: The spleen acts as a site for immune responses, where lymphocytes interact with antigens presented by dendritic cells.
Blood Filtration and Clearance:
- Blood Filter: The spleen filters the blood, removing debris, microorganisms, and blood-borne antigens.
- Removal of Old Blood Cells: Macrophages in the spleen phagocytose and remove aged red blood cells and platelets.
- Clearance of Damaged Cells: The spleen plays a role in the clearance of damaged or defective platelets and neutrophils.
Hemopoiesis:
- Fetal Hemopoiesis: During fetal development, the spleen is involved in the production of blood cells.
- Adult Hemopoiesis: In adults, hemopoiesis primarily occurs in the bone marrow, but the spleen can resume its hemopoietic function if needed.