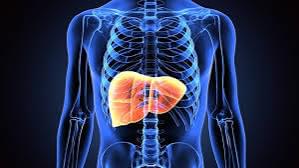
Acute liver failure (ALF), also known as fulminant hepatic failure, is a severe medical condition where the liver abruptly ceases to function. This sudden loss of liver function can occur within days or weeks without any prior history of liver disease, making it both a rare and critical condition that requires urgent medical attention. The primary focus of this article is to understand this serious health condition, its various types, potential causes, observable symptoms, and the available treatment options.
Table of Contents
What is Acute Liver Failure?
Acute liver failure is a rapid deterioration of the liver’s function characterized by the sudden onset of hepatic encephalopathy (a condition that affects brain function) and coagulopathy (a condition that affects blood clotting) in individuals without pre-existing liver disease. It’s essential to know that ALF is less common than chronic liver failure, which develops more slowly. However, ALF poses a significant threat due to its rapid progression and potential complications.
Causes of Acute Liver Failure
There are numerous potential causes of acute liver failure. Here are the most common ones:
1. Overdose of Medications: An overdose of certain medications, such as acetaminophen (also known as paracetamol), is one of the most common causes of ALF in many regions, including the United States.
2. Viral Infections: Certain viral infections, mainly hepatitis viruses like hepatitis A, B, and E, can lead to ALF. Other viruses such as Epstein-Barr, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus can also cause ALF.
3. Autoimmune Hepatitis: This is a disease where the body’s immune system attacks liver cells, causing inflammation and injury, leading to Acute Liver Failure.
4. Toxins: Certain toxins, including poisonous mushrooms and industrial chemicals, can cause Acute Liver Failure.
5. Metabolic Disorders: Rare metabolic diseases like Wilson’s disease and acute fatty liver of pregnancy can cause Acute Liver Failure.
Symptoms of Acute Liver Failure
Identifying the symptoms of Acute Liver Failure early can potentially save lives. Here are some signs to look out for:
1. Jaundice: This is a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes resulting from high levels of bilirubin, a yellow-orange substance, in the body.
2. Pain in the Abdomen: One may experience pain in the upper right part of the abdomen, which is where the liver is located.
3. Nausea and Vomiting: These are common symptoms of many illnesses, including ALF.
4. General Malaise: A general sense of feeling unwell or ill is another symptom of ALF.
5. Mental Confusion: In severe cases, ALF can lead to disorientation, confusion, and even a coma.
Diagnosis of Acute Liver Failure
Diagnosing ALF involves a series of tests and procedures. The first step is a physical examination where the healthcare professional checks for visible signs and enquires about the symptoms. The patient’s diet, lifestyle, and health history are also evaluated.
Some of the tests and procedures that may be carried out include:
1. Blood Tests: These tests measure the levels of liver enzymes, proteins, and bilirubin in the blood. They can show signs of liver disease, its severity, and liver failure.
2. Imaging Tests: An ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI can reveal information about the size, shape, and texture of the liver, helping to identify inflammation, growths, and fibrosis.
3. Liver Biopsy: This is a minor procedure where a small tissue sample from the liver is taken for lab testing. It can help check for cancer, confirm cirrhosis, and determine the cause of the condition.
Treatment of Acute Liver Failure
The treatment for ALF depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For instance, antiviral medications are used to treat viral hepatitis, while corticosteroids and immunosuppressants are used for autoimmune diseases. Often, lifestyle changes are the primary treatment for liver disease, especially for conditions caused by excess fat storage, alcohol, or other toxins.
In severe cases, where the liver cannot recover, a liver transplant may be the only solution. This involves replacing the diseased liver with a healthy one from a donor.
Complications of Acute Liver Failure
ALF can lead to serious complications, including:
1. Cerebral Edema: This is a condition where there is an excess accumulation of fluid in the brain, leading to increased pressure, disorientation, severe mental confusion, and seizures.
2. Bleeding Disorders: A failing liver cannot produce enough clotting factors, leading to increased bleeding and bruising.
3. Infections: People with ALF are more prone to infections, especially in the blood and respiratory and urinary tracts.
4. Kidney Failure: ALF can affect kidney function, leading to kidney failure. This is particularly common in cases of acetaminophen overdose, which damages both the liver and kidneys.
Prevention of Acute Liver Failure
Prevention of ALF involves taking care of your liver by following these guidelines:
1. Medication Guidelines: Always follow the recommended dosage for all medications, including over-the-counter ones. Consult your healthcare provider if you have any doubts.
2. Limit Alcohol Consumption: If you choose to drink, do so in moderation. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to ALF.
3. Practice Safe Sex and Hygiene: Practicing safe sex and good personal hygiene can help prevent the spread of hepatitis viruses.
4. Avoid Toxic Substances: Be sure to use personal protective equipment when using toxic substances, such as insecticides, fungicides, and other chemicals.
5. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which can cause ALF.
Prognosis and Outlook
While the prognosis for ALF varies depending on the cause and the individual’s overall health, early detection and treatment can often reverse the condition. However, in severe cases where cirrhosis or liver failure has set in, a liver transplant may be the only option.
Living with ALF can be challenging, but with the right medical attention and lifestyle changes, individuals can manage the condition and lead a healthy life. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect any symptoms or need guidance on managing liver health.
Remember, your liver is a vital organ that plays a critical role in your body’s overall health. Hence, taking care of your liver is an integral part of maintaining your wellbeing.